Upgrading GeoServer¶
Warning
Be aware that some upgrades are not reversible, meaning that the data directory may be changed so that it is no longer compatible with older versions of GeoServer. See Migrating a data directory between versions for more details.
Upgrade Process¶
The general GeoServer upgrade process is as follows:
Back up the current data directory. This can involve simply copying the directory to an additional place.
Make sure that the current data directory is external to the application (not located inside the application file structure).
Check the GeoServer Server status page to double check the data directory location.
Make a note of any extensions you have installed.
The GeoServer page provides a Modules tab listing the modules installed.
Some extensions include more than one module, as an example the WPS extension is listed as
gs-wps-coreandgs-web-wps.
Uninstall the old version and install the new version.
Download maintenance release to update existing installation.
There should generally be no problems or issues updating data directories between patch versions of GeoServer (for example, from 2.28.0 to 2.28.1 or vice versa).
It is also generally possible to revert a minor update and maintain data directory compatibility.
Download stable release when ready to upgrade.
There should rarely be any issues involved with upgrading between minor versions (for example, from 2.27.x to 2.28.x).
Upgrading between major versions of GeoServer (for example from 2.28 to 3.0) may not be reversible, since newer versions of GeoServer may make backwards-incompatible changes to the data directory.
Be sure to download and install each extension used by your prior installation.
Make sure that the new installation continues to point to the same data directory used by the previous version.
How often should I upgrade GeoServer¶
GeoServer operates with a time boxed release cycle, maintaining “stable” and “maintenance” releases, over the course of a year.
Plan to upgrade GeoServer at least twice a year as new stable releases are made.
Once the release you are using has entered “maintenance” it is a good idea to upgrade (before the release is no longer supported).
GeoServer provides some overlap between “stable” and “maintenance” releases to provide you a window of opportunity to upgrade between supported versions.
GeoServer security policy indicates each release is supported with bug fixes for a year, with releases made approximately every two months.
You may also contact our service providers for extended support beyond this timeframe.
Monitor release announcements in case a new release is made that provides “Security Considerations” guidance.
It is always advisable to stay up to date with security patches. The blog post will indicate when the update is urgent, and several releases will be made concurrently (for both stable and maintenance) when urgent action is required.
Note
Do not wait for a release to fall out of support before upgrading. Doing so places you in a position of having to perform an upgrade quickly with a lot of pressure in the event a security vulnerability is announced.
Note
If you do see several releases being made concurrently, in response to an urgent vulnerability, the developers will not be in a position to tell you what is going on. Their goal is to provide you an opportunity to upgrade prior to public disclosure.
Those seeking more information, or with a legal obligation to be informed, are welcome to volunteer on the geoserver-security email list. See Security Process for details on how to participate.
Troubleshooting¶
Forgetting to include an Extension¶
The most common difficulty when updating GeoServer is forgetting to include an extension.
This may result in the application being unable to start up, as it attempts to read a configuration file without the corresponding extension that understands the setting.
This may result in missing functionality, for example forgetting to install an output format will result in that format not being available for use.
Upgrading more than one version¶
If it has been a while since you have upgraded GeoServer be cautious when upgrading from an unsupported release of GeoServer all the way to the latest release. Consider first trying a quick update in one go, but be prepared to perform a sequential update to each major release in turn, applying the guidance in the section below at each stage.
Note
Trying a quick update GeoServer 2.26.0 to GeoServer 2.28.0
Back up the current data directory
Check the Download page and download the target release:
GeoServer 2.28.0
You may also make a note of the version of Java to download:
OpenJDK 17
Perform the upgrade in one go, checking the guidance on this page for any work to perform.
The application property ENTITY_RESOLUTION_UNRESTRICTED is noted, if you are affected by a change in XML Parsing. This should only affect Application Schema that made use of the Unrestricted XML External Entity Resolution setting.
The application property GEOSERVER_DATA_DIR_LOADER_ENABLED is noted as an option if any deadlock occurs during startup due to an improvement in startup performance.
A wide a range of Content Security Policy restrictions have been introduced, and very clear instructions noted to double check proxy_base_url is correct (as the GeoServer user interface will now detect and block a misconfigured system). The application property org.geoserver.web.csp.strict=false is available to temporarily disable this safety measure if you are locked out.
Installation of Java 11 is required.
Out of an abundance of caution testing raster layers is advisable due to wholesale change of the image processing engine.
Review the logs during startup, and test to ensure the application is working as expected.
If you encounter problems consider planning a sequential update as in the next example.
Note
Planning a sequential update from GeoServer 2.26.0 to GeoServer 2.28.0
Check the Download page and download the releases needed to make the transition:
GeoServer 2.26.4
GeoServer 2.27.3
GeoServer 2.28.0
You may also make a note of the version of Java to download:
OpenJDK 17
Perform each update in sequence, checking the guidance on this page for any work to perform.
Updating from GeoServer 2.26.0 to GeoServer 2.26.4
The application property ENTITY_RESOLUTION_UNRESTRICTED is noted, if you are affected by a change in XML Parsing. This should only affect Application Schema that made use of the Unrestricted XML External Entity Resolution setting.
Review the logs during startup, and test to ensure the application is working as expected.
Updating from GeoSerer 2.26.4 to GeoServer 2.27.3.
The application property GEOSERVER_DATA_DIR_LOADER_ENABLED is noted as an option if any deadlock occurs during startup due to an improvement in startup performance.
A wide a range of Content Security Policy restrictions have been introduced, and very clear instructions noted to double check proxy_base_url is correct (as the GeoServer user interface will now detect and block a misconfigured system). The application property org.geoserver.web.csp.strict=false is available to temporarily disable this safety measure if you are locked out.
Review the logs during startup, and test to ensure the application is working as expected.
Updating from GeoServer 2.27.3 to GeoServer 2.28.0.
Installation of Java 11 is required.
Out of an abundance of caution testing raster layers is advisable due to wholsale change of the image processing engine.
Review the logs during startup, and test to ensure the application is working as expected.
Upgrading GeoServer 3 Guidance¶
GeoServer 3.0.x is scheduled for release in March, 2026.
Tomcat 10.1 or Tomcat 11.0 Required¶
GeoServer 3.0 makes the transition to Jakarata EE Servlet 6.0.0 and requires Tomcat 10.1 or Tomcat 11.0 for those using WebArchive distribution.
H2 Datastore Removal (GeoServer 3.0 and newer)¶
As of GeoServer 3.0, the H2 datastore extension (gs-h2) has been removed and is no longer available for use
as a GeoServer vector datastore.
If your installation contains any H2-based datastores, migrate those layers to another supported datastore before upgrading to GeoServer 3.0.
After upgrading, review the startup logs for missing datastore errors and verify all layers and services load as expected.
Upgrading GeoServer 2 Guidance¶
GeoServer 2.0.x was first released in October 29, 2009.
Java 17 and ImageN (GeoServer 2.28.0)¶
As of GeoServer 2.28.0, Java 17 is now the minimum required Java version to run GeoServer.
Additionally, the image processing engine is now ImageN:
JAI-Ext related settings are gone from the UI (e.g. configuring if a certain operation should use JAI-Ext or not, from now on, it will use ImageN).
JAI native settings have been removed (ImageN is pure Java).
One notable change in the configuration is that the
USE_JAI_IMAGEREADparameter is now calledUSE_IMAGEN_IMAGEREAD.
This USE_IMAGEN_IMAGEREAD` parameter is used by image mosaic and a few other coverage readers,
and is normally called “deferred loading” in the UI.
GeoServer will migrate the parameter name automatically when layers are saved,
and compatibility with REST scripts using the old name is preserved.
If you want to migrate the data directory to the new parameter in bulk, look up all the coverage.xml
files and replace the parameter name in them. For example, on Linux, the following command will
perform a migration:
find <GEOSERVER_DATA_DIR> -name coverage.xml -exec sed -i 's/USE_JAI_IMAGEREAD/USE_IMAGEN_IMAGEREAD/g' {} \;
MapML Multi-Layer As Multi-Extent Configuration (GeoServer 2.27 and newer)¶
As of GeoServer 2.28, the configuration option for MapML Multi-Layer as Multi-Extent has been moved from the WMS Administration page to the Publishing tab of the Layer Group configuration. Backwards compatibility with previously configured MapML implementations is maintained through the population of Layer Group metadata if the option was previously enabled in the WMS Administration page. For more information, see Installation.
FreeMarker Template Method Access (GeoServer 2.27 and newer)¶
As of GeoServer 2.27, FreeMarker templates are now restricted from accessing methods related to certain sensitive classes to mitigate the impact of malicious templates. Most templates that can be modified by administrators will also be limited to only accessing getter methods. For more information about this, see Accessing Instance Methods.
The following is an example of the exception message seen when processing a template that previously worked but is blocked by the new restrictions:
Caused by: freemarker.core.InvalidReferenceException: The following has evaluated to null or missing: ==> features[0].type.catalog [in template "content_en_US.ftl" at line 1, column 3]
Content Security Policy (GeoServer 2.27 and newer)¶
The Content-Security-Policy HTTP response header are now enabled by default in order to mitigate cross-site scripting and clickjacking attacks. The default header value asks the browser to block the use of inline JavaScript in all HTML output except in cases where it is required (e.g., OpenLayers maps).
It is anticipated that future work may further restrict the default policy in the interests of safety.
It is expected that the web administration console functions correctly, along with extensions and community modules.
Before starting double check that your proxy base url setting is correct (including HTTP/HTTPS differences).
Warning
CSP restrictions will detect if this information is inconsistent, preventing the user interface from functioning.
If you have problems with the administration console being frozen or not working, please see User interface non-responsive for details on how to restore access during troubleshooting.
If you encounter any CSP problems please let us know, as an open-source project we depend on public feedback and testing to report CSP problems found.
With these improved CSP safety measures GeoServer may now detect vulnerabilities in your environment that were previously undetected.
Managing CSP restrictions in GeoServer:
When using inline JavaScript in custom FreeMarker templates for WMS GetFeatureInfo HTML output will require use of GEOSERVER_FEATUREINFO_HTML_SCRIPT application property.
If you experience issues with static web files or custom classes/plugins generating HTML output may need to update their settings.
For more information, see Content-Security-Policy.
Note
It is recommended that static web files be disabled if they are not necessary in order to mitigate cross-site scripting attacks. For more information, see Serving Static Files.
GeoServer provides tools for administrators to control content security policy headers, see GeoServer Security section on Content Security Policy Reference for very detailed information.
Faster Startup for Large Catalogs (GeoServer 2.27 and newer)¶
Starting in GeoServer 2.27.0, the configuration loading process has been optimized for faster startup times, particularly for large catalogs and network filesystem deployments.
With this enhancement, catalog and configuration loading is now up to 3× faster on local disks and up to 10× faster on network filesystems.
Potential Considerations:
Check Compatibility: Although the new loader is a drop-in replacement, verify that your existing configurations and extensions work as expected. Testing in a staging environment before deploying to production is recommended.
Configuration:
No additional configuration is required for standard setups. However, if you encounter any issues, you can disable the optimized loader by setting the GEOSERVER_DATA_DIR_LOADER_ENABLED=false environment variable or system property.
For additional information see Data directory loader documentation.
Keystore password link (GeoServer 2.26 and newer)¶
The Password page link to Keystore password forgotten now directly links to the REST API endpoint, allowing the value to be read in your browser.
With this change it is no longer necessary to generate a masterpw.info when upgrading an older data directory. If this file is present from an earlier upgrade it is still considering a security warning noted on the welcome page.
ENTITY_RESOLUTION_UNRESTRICTED application property (GeoServer 2.26.4 and newer)¶
The global setting Unrestricted XML External Entity Resolution has been repalced with the ENTITY_RESOLUTION_UNRESTRICTED application property.
For more information see External Entities Resolution.
REST API URL Checks (GeoServer 2.26 and newer)¶
URLChecks are now available for REST API upload.
Use the existing URL Checks page to add any locations or directories for use.
GRIB Layers (GeoServer 2.26 and newer)¶
GeoServer 2.26 upgraded underlying Unidata NetCDF libraries, from 4.x to 5.x, which includes internal changes to how GRIB files are interpreted (mapping tables and GRIB parameters interpretation changes). This results in the underlying library giving some variables a different name, as well as interpreting the temporal variables differently (e.g., from period to instant, and changing the number of available times as a consequence).
Due to the above compatibility issues, some layers based on underlying GRIB datasets may stop working properly after the upgrade. If that is the case, the recommended action is to do a backup before doing the upgrade and then reconfigure the layers.
Backup¶
Backup the GeoServer data directory
Backup eventual DB tables being used as catalog for the GRIB Datasets (That could be needed if ImageMosaic of GRIB have been configured, storing the mosaic index on DB)
Backup the index file automatically generated by GRIB/NetCDF library for the involved GRIB files (i.e. *.gbx9, *.ncx3; *.ncx4)
Basic cleanup¶
Remove any auxiliary/cache file associated with the underlying GRIB file (assuming the file is named gribfile.grib2):
gribfile.ncx3
gribfile.ncx4
gribfile.gbx9
.gribfile_hash folder (if not previously deleted) either located beside the original file, or within the configured NETCDF_DATA_DIR (if defined).
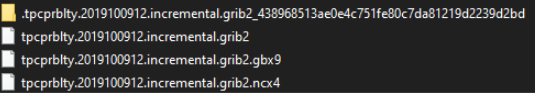
The screenshot below represents an actual example of a tpcprblty.2019100912.incremental.grib2 file with related auxiliary/cache files
Additional steps needed in case of ImageMosaic of GRIBs¶
Remove any automatically created ImageMosaic configuration file within the ImageMosaic root folder. Assuming the underlying ImageMosaic was named mosaicM, containing coverages related to VariableA, VariableB, VariableC, …:
VariableA.properties, VariableB.properties, VariableC.properties, …
VariableAsample_image.dat, VariableBsample_image.dat, VariableCsample_image.dat, …
mosaicM.xml
If using a datastore.properties connecting to an actual DB, clean up the tables from the DB
Assuming that all the GRIB files belonging to the same ImageMosaic are affected by the same issue, you can delete the related tables and allow the imageMosaic reconfiguration to recreate them.
Based on the above example, the naming convention is that granules for VariableA are stored on table named VariableA and so on.
Recreate the indexer.xml and _auxiliary.xml file as reported in the NetCDF documentation . (At the end, GRIB file are served through the NetCDF libraries)
Configuration cleanup¶
The GeoServer configuration refers to the “native name” of the variables, as reported by the underlying libraries, which might have changed during the upgrade.
If you are lucky, the following might help you to reconfigure the layers:
Open the
coverage.xmlfile of the affected layer and check thenativeNameandnativeCoverageName`attributes, to the new variable name (you can pick it up from tools like ToolsUI or Panoply).Reload the GeoServer configuration, either by restarting the GeoServer service or by using the GeoServer Admin UI.
Check if the layer is now working.
If the above did not help, then a full cleanup of the GeoServer configuration is needed:
Remove the affected store, either Mosaic or GRIB Store, referring to the problematic GRIB files.
Follow up standard procedure to delete affected stores and underlying layer
Alternatively, consider using REST APIs to do that by referring to the DELETE method for
/workspaces/{workspace}/coveragestores/{store}. Use?recurse=true&purge=metadatato delete layers and auxiliary files as well
Recreate the stores and layers using the known procedures.
Disk Quota validation query (GeoServer 2.25.4 and newer)¶
When using the JDBC Disk Quota:
Validation query for
H2is limited toSELECT 1.Validation query for
Oracleis limited toSELECT 1 FROM DUAL.Validation query for other JDBC formats receive a warning in the logs if it is not one of the common examples above.
Note
If you find your JDBC Disk Quota is no longer loaded on startup: check the logs for message about validation query, edit the configuration, and restart.
External Entity Allow List default (GeoServer 2.25 and newer)¶
The external entity allow list has changed to the following default locations:
www.w3.orgschemas.opengis.netwww.opengis.netinspire.ec.europa.eu/schemasproxy base url if configured
The external entity allow list is an important setting from a security standpoint. This update changes its use from a recommended best practice to a default covering the most common locations used for OGC web services.
Note
In general only application schema extension users need to update this setting.
Note
To restore the previous behavour use system property ENTITY_RESOLUTION_ALLOWLIST=* to allow external entity resolution from any http or https location.
For more information, including how to add additional allowed locations see External Entities Resolution.
FreeMarker Template HTML Auto-escaping (GeoServer 2.25 and newer)¶
As of GeoServer 2.25, the FreeMarker library’s HTML auto-escaping feature will be enabled by default to prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in WMS GetFeatureInfo HTML output when using the default FreeMarker templates and WMS service settings. Some users may experience incorrectly escaped HTML output when using custom templates or if HTML tags are stored in vector data stores.
See the FreeMarker Template Auto-escaping page for information about the limitations of this feature and for instructions to disable this feature and delegate to the WMS service setting which defaults to disabling HTML auto-escaping.
Spring Security Strict HTTP Firewall (GeoServer 2.25 and newer)¶
As of GeoServer 2.25, Spring Security’s StrictHttpFirewall will be enabled by default which will provide stronger default protection, particularly against potential path traversal vulnerabilities.
In some cases valid requests may be blocked if the names of GeoServer resources (e.g., workspaces) contain certain special characters and are included in URL paths. See the Spring Security Firewall page for instructions to disable the strict firewall and revert to the DefaultHttpFirewall used by earlier versions.
WCS ArcGRID output format removal (GeoServer 2.24 and newer)¶
The ArcGRID output format for WCS has been removed in GeoServer 2.24.0. If you have been using this format, you will need to switch to another text based format, such as GML coverage, or can get back the ArcGRID format by installing the WCS GDAL community module and use a configuration like the following (please adapt to your system):
<ToolConfiguration>
<executable>gdal_translate</executable>
<environment>
<variable name="GDAL_DATA" value="/usr/local/share/gdal" />
</environment>
<formats>
<Format>
<toolFormat>AAIGrid</toolFormat>
<geoserverFormat>ArcGrid</geoserverFormat>
<fileExtension>.asc</fileExtension>
<singleFile>true</singleFile>
<mimeType>application/arcgrid</mimeType>
</Format>
</formats>
</ToolConfiguration>
Disk Quota HSQL DB usage (GeoServer 2.24 and newer)¶
As of GeoServer 2.24, H2 DB support will be replaced with HSQL DB for Tile Caching / Disk Quota store.
H2 option under “Disk quota store type” and “Target database type” is replaced with HSQL.
The default store type will be in-process HSQL.
Existing installations with in-process H2 selection will automatically be migrated to in-process HSQL. Old H2 database files will remain in
gwc/diskquota_page_store_h2/under the data directory. You may delete those or leave them for a possible downgrade.Important: Existing installations with external H2 database selection will not be migrated automatically. You will get an error message at startup and disk quota will be disabled, unless you use a plugin/extension with H2 dependency. But other features of GeoServer will keep working. You can go to Disk Quota page and configure an external HSQL database or switch to in-process HSQL. In case you want to keep using H2 as an in-process/external database, you can add H2 store plugin or any other extension or plugin that has H2 dependency.
GeoServer installations with extensions/plugins having H2 dependency will still have H2 option under “Disk quota store type” and “Target database type”.
URL Checks for remote requests control (GeoServer 2.24 and newer)¶
As of GeoServer 2.24, remote requests control has been added, and enabled by default, in GeoServer. This feature allows administrators to control which remote requests are allowed to be made to GeoServer. By default, no authorizations are included, thus GeoServer will deny remote requests originating from user interaction. In particular, the following use cases are affected:
WMS operations with remotely fetch styles (
sldparameter) and style referencing remote icons (in general, icons outside of the data directory). As a reminder, when a remote icon is not found, GeoServer will fall back to a default icon, a gray square with a black border.WMS “feature portrayal” with dynamic remote WFS references provided in the request (
REMOTE_OWS_TYPEandREMOTE_OWS_URLparameters).WPS remote inputs via either GET or POST request (e.g., remote GeoJSON file source).
The list of locations that are safe to contact can be configured using the URL Checks page.
Log4J Upgrade (GeoServer 2.21 and newer)¶
As of GeoServer 2.21, the logging system used by GeoServer has been upgraded from Log4J 1.2 to Log4J 2.
GeoServer now uses
xmlfiles for the built-in logging profiles (previouslypropertiesfiles were used).The built-in logging profiles are upgraded with
xmlfiles:DEFAULT_LOGGING.xml DEFAULT_LOGGING.properties.bak
A backup of the prior
propertiesfiles are created during the upgrade process. If you had previously made any customizations to a built-in profiles these backup files may be used as a reference when customizing the xml file.Log4J 2 does have the ability to read Log4j 1.2 properties files although not all features are supported.
Any custom
propertiesfiles you created will continue to be available for use.If necessary you can recover a customization you performed to a built-in logging profile by restoring to a different filename. To recover a customization from
PRODUCTION_LOGGING.properties.bakrename the file toPRODUCTION_LOGGING.properties.baktoCUSTOM_LOGGING.properties.If you never plan to customize the built-in logging profiles the
UPDATE_BUILT_IN_LOGGING_PROFILES=truesystem property will always ensure you have our latest recommendation.
JTS Type Bindings (GeoServer 2.14 and newer)¶
As of GeoServer 2.14, the output produced by REST featuretype and structured coverage requests using a different package name (org.locationtech instead of com.vividsolutions) for geometry type bindings, due to the upgrade to JTS (Java Topology Suite) 1.16.0. For example:
Before:
...
<attribute>
<name>geom</name>
<minOccurs>0</minOccurs>
<maxOccurs>1</maxOccurs>
<nillable>true</nillable>
<binding>com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Point</binding>
</attribute>
...
After:
...
<attribute>
<name>geom</name>
<minOccurs>0</minOccurs>
<maxOccurs>1</maxOccurs>
<nillable>true</nillable>
<binding>org.locationtech.jts.geom.Point</binding>
</attribute>
...
Any REST clients which rely on this binding information should be updated to support the new names.
GeoJSON encoding (GeoServer 2.6 and newer)¶
As of GeoServer 2.6, the GeoJSON produced by the WFS service no longer uses a non-standard encoding for the CRS. To re-enable this behavior for compatibility purposes, set GEOSERVER_GEOJSON_LEGACY_CRS=true as a system property, context parameter, or environment variable.