Content Security Policy¶
The Content Security Policy page controls how GeoServer prepares the Content-Security-Policy (CSP) HTTP response headers, used to mitigate cross-site scripting and clickjacking attacks.
Default Configuration¶
The default CSP configuration is intended to support many GeoServer use cases and allow users to securely run GeoServer without having to modify the configuration. It may be updated in future releases to fix bugs, support new features or enhance security.
The default header value for most GeoServer requests will be:
base-uri 'self'; default-src 'none'; child-src 'self'; connect-src 'self'; font-src 'self'; img-src 'self' data:; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; script-src 'self'; form-action 'self'; frame-ancestors 'self';
The 'unsafe-inline' and 'unsafe-eval' sources will be added to the script-src
directive only for specific requests that may require unsafe JavaScript.
Note
While the 'self' script source should be sufficient to prevent most reflected cross-site
scripting, it does leave the possibility of stored cross-site scripting by administrators
with permissions to upload static web files. It is anticipated that future work will further
restrict the default policy to completely disable JavaScript for most requests. See the
Serving Static Files page for instructions to disable that feature if it is not needed.
The default configuration may be updated as necessary by the GeoServer developers.
The current CSP configuration is stored in the GeoServer data directory file security/csp.xml.
The default CSP configuration will be stored in the file security/csp_default.xml.
It is important that administrators do NOT modify csp_default.xml. In order to detect when new GeoServer releases update the default configuration, GeoServer will check the current default configuration against the configuration in csp_default.xml. If they are found to be different:
csp.xmlwill be updated with the policies from the new default configuration if they have not been changed from the old default configuration. Other settings will not be changed.csp_default.xmlwill be updated with the new default configuration.
Configuring CSP¶
Navigate to to manage and configure the CSP header.
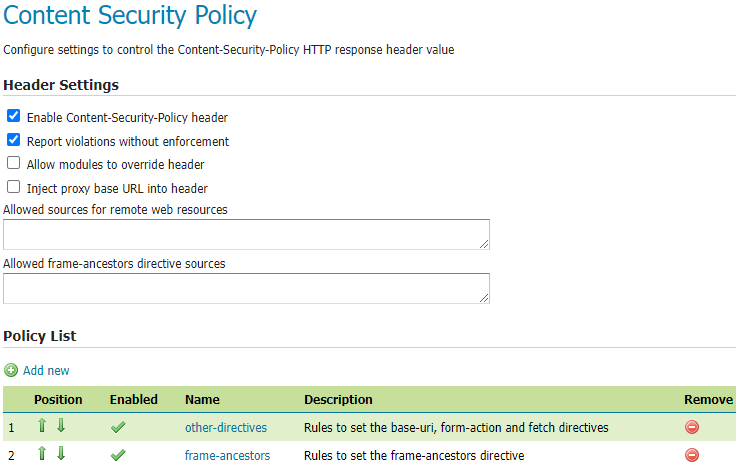
CSP Configuration¶
Use the Enable Content-Security-Policy header checkbox to enable/disable this feature. This setting will enable/disable the CSP set by Wicket or any other modules setting their own CSP unless Allow modules to override header is set to true.
Use the Report violations without enforcement checkbox to switch the header name from
Content-Security-Policy to Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only. This will tell the browser
to report CSP violations without enforcing their effects to allow administrators and developers to
experiment with different policies. This setting will apply to the CSP set by Wicket or any other
modules setting their own CSP unless Allow modules to override header is set to true.
Use the Allow modules to override header checkbox to allow Wicket web pages and other
modules to completely overwrite the header that is set by this configuration. By default, when the
CSP header is set by another component, GeoServer will attempt to append any non-fetch directives
from the old header value that are not already in the new value. This is primarily intended to add
the form-action and frame-ancestors directives to Wicket’s CSP header.
Use the Inject proxy base URL into header checkbox to inject the proxy base URL into
the form-action directive and all fetch directives that normally allow 'self'. This is only
necessary for certain use cases where web browsers are able to access a GeoServer host directly
rather than through the proxy and the HTML response contains absolute URLs to the proxy base URL.
This does not guarantee that other browser restrictions will not prevent the page from functioning.
Enabling this with a proxy base URL set to
https://geoserver.orgwould change the header value at the top of this page to:base-uri 'self'; default-src 'none'; child-src 'self' https://geoserver.org; connect-src 'self' https://geoserver.org; font-src 'self https://geoserver.org'; img-src 'self' https://geoserver.org data:; style-src 'self' https://geoserver.org 'unsafe-inline'; script-src 'self' https://geoserver.org; form-action 'self' https://geoserver.org; frame-ancestors 'self';
Use the Allowed sources for remote web resources text field to add sources to the
font-src, img-src, style-src, and script-src directives for static web files (if
not disabled by system property) and for WMS GetFeatureInfo HTML output (if enabled by system
property). This is intended to make it easier to allow loading these resources from a CDN or any
other remote host. Only trusted hosts should be added here to prevent cross-site scripting
attacks.
Setting this to
'self' https://geoserver.orgwould set the following header value for an HTML file in the static files directory:base-uri 'self'; default-src 'none'; child-src 'self'; connect-src 'self'; font-src 'self' https://geoserver.org; img-src 'self' https://geoserver.org data:; style-src 'self' https://geoserver.org 'unsafe-inline'; script-src 'self' https://geoserver.org; form-action 'self'; frame-ancestors 'self';
Note
The geoserver.csp.remoteResources system property will override this field if it has been set.
Use the Allowed form-action directives sources text field to control the sources of the
form-action directive. This is intended to make it easier for administrators to allow specific remote
hosts to submit forms to. This can be useful for cases where form submissions may redirect the browser to
a URL that does not exactly match the submitting page and can also help where GeoServer authentication is
handled by an external service. Only trusted hosts should be added here to prevent cross-site scripting
attacks from submitting sensitive data to an attacker-controlled site.
Setting this to
'self' https://geoserver.orgwould change the header value at the top of this page to:base-uri 'self'; default-src 'none'; child-src 'self'; connect-src 'self'; font-src 'self'; img-src 'self' data:; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; script-src 'self'; form-action 'self' https://geoserver.org; frame-ancestors 'self';
Note
The geoserver.csp.formAction system property will override this field if it has been set.
Warning
The web interface will block setting this field to a value containing 'none' in order to prevent an
administrator from accidentally triggering a denial-of-service. If an administrator wants to disable all
form submissions, the full CSP header value can be configured in a rule or the configuration file can be
uploaded through the REST Resources API or modified manually in the data directory.
Use the Allowed frame-ancestors directive sources text field to control the sources of
the frame-ancestors directive. This is intended to make it easier for administrators to allow
specific remote hosts to load GeoServer content in frames. Only trusted hosts should be added
here to prevent clickjacking attacks.
Setting this to
'self' https://geoserver.orgwould change the header value at the top of this page to:base-uri 'self'; default-src 'none'; child-src 'self'; connect-src 'self'; font-src 'self'; img-src 'self' data:; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; script-src 'self'; form-action 'self'; frame-ancestors 'self' https://geoserver.org;
Note
The geoserver.csp.frameAncestors system property will override this field if it has been set.
Note
For the form-action and frame-ancestors text fields and system properties, HIDE is a special
keyword that can be used to hide their respective directive from the CSP header. Also, 'self' will be
automatically added to the directive when a non-empty string is provided that is not HIDE and does
not contain 'self' or 'none' (e.g., setting the value to https://geoserver.org will cause
'self' https://geoserver.org to be used in the CSP).
Configuring Policies¶
Each policy contains the rules and directives to set a single CSP header value. When there are CSP directives from multiple policies, the directives will be concatenated into a single line using commas rather than setting multiple Content-Security-Policy headers. If a value for a specific directive is defined in multiple policies, web browsers will use the strictest value set for that directive.
The button for adding policies can be found at the top of the Policy List table and a policy can be edited by clicking on its name in the table or removed by clicking on the remove icon at the end of the policy’s row in the table. Policy positions can also be changed by using the up/down arrows or by dragging and dropping the rule’s row in the table.
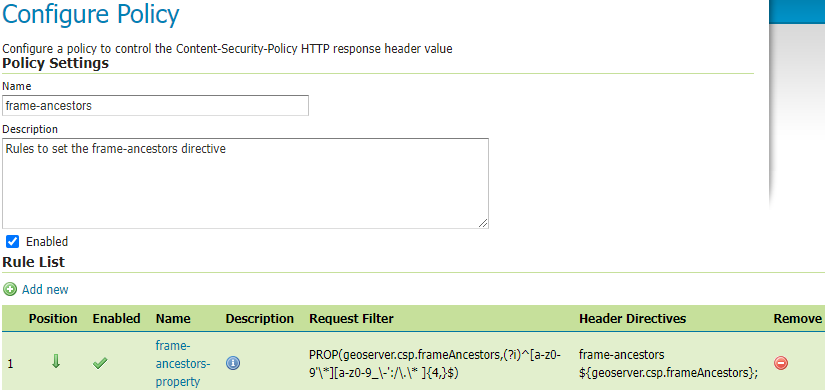
CSP Policy Configuration¶
A unique name must be provided in the Name text field when adding a new policy.
The Description text field provides an optional description to help administrators understand what the policy does.
The Enabled checkbox will enable/disable the policy.
Note
After saving a policy, make sure to save/apply the configuration.
Configuring Rules¶
Each rule contains a filter to match against user requests and the CSP directives to add to the header value for matching requests. Rules will be checked in order against incoming requests and only the first matching rule in each policy will be applied. If no rule in a policy matches the request, then no directives will be added to the CSP header from that policy. If the matching rule has no directives defined, then preceding rules will be checked until the first rule is found that has directives and no directives will be added if no such rule exists.
The button for adding rules can be found at the top of the Rule List table and a rule can be edited by clicking on its name in the table or removed by clicking on the remove icon at the end of the rule’s row in the table. Rule positions can also be changed by using the up/down arrows or by dragging and dropping the rule’s row in the table.
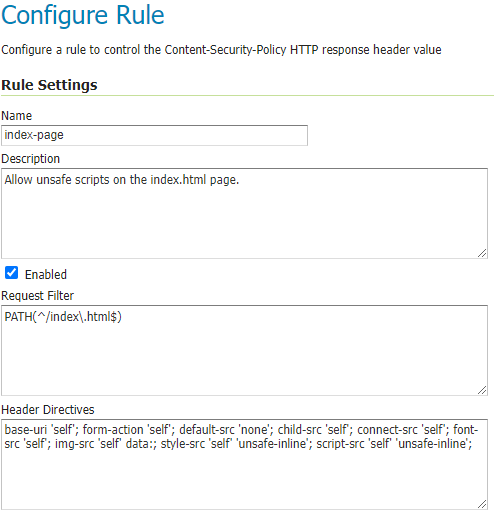
CSP Rule Configuration¶
A name that is unique among the rules within the specific policy must be provided in the Name text field when adding a new rule.
The Description text field provides an optional description to help administrators understand what the rule does.
The Enabled checkbox will enable/disable the rule.
The Request Filter text field contains the filter to apply to each user request to determine whether to add this rule’s directives to the CSP header value. (see Request Filters below)
The Header Directives text field contains the CSP directives to add to the header value when a request matches this rule’s filter. (see Header Directives below)
Note
After saving a rule, make sure to save the policy and then save/apply the configuration.
Request Filters¶
The filter contains a string of predicates concatenated with the string AND and the rule’s
directives will be applied to a request only if all of the predicates match the request. There
are three types of predicates that can be used:
PATH(regex): Returns true if the URL-decoded request path matches the regular expression. The regex will be tested against the path that is relative to GeoServer’s context root and starting with a forward slash.
Example:
PATH(^/([^/]+/){0,2}wms/?$)PARAM(key_regex,value_regex): Returns true if all query parameters with a URL-decoded key that match the key_regex have a URL-decoded value that match the value_regex. The value regex will be tested against an empty string if no query parameters matched the key regex.
Example:
PARAM((?i)^service$,(?i)^wms$)
PROP(key,value_regex): Returns true if the value for the property key matches the regex. The key is case-sensitive and must contain the string
GeoServer,GeoTools, orGeoWebCacheanywhere in the key (case-insensitive). The regex will be tested against an empty string if the property is not set. This is primarily intended for the default configuration and may not be useful to administrators.Example:
PROP(GEOSERVER_CONSOLE_DISABLED,(?i)^(?!true$).*$)
Note
The
(?i)at the beginning of the regular expression will use case-insensitive matching and enclosing the pattern inside of the^$characters will match the entire string. See the Regular Expressions Tutorial for more information about how to use Java regular expressions.
Leaving the filter blank will cause this rule to match all requests and should only be used on the last rule in a policy since any additional rules would never be checked.
Header Directives¶
Warning
GeoServer gives administrators complete control over the CSP header directives and sources and does not attempt to parse or validate them so it is the administrator’s responsibility to verify that the header is working as intended when modifying this field. See System Administrator CSP Settings for detailed information about valid Content Security Policy header directives and sources.
Property keys can be used in the directives in the form ${key} and they will be replaced with
the property’s value before being written to the header. Property keys must contain GeoServer,
GeoTools, or GeoWebCache (case-insensitive) and property values must not contain special
characters that are not allowed in valid CSP sources. Properties can be set either via Java system
property, command line argument (-D), environment variable or web.xml init parameter.
geoserver.csp.remoteResources and geoserver.csp.frameAncestors are special property keys
that will use the value from their corresponding fields in the CSP configuration if they are not
defined as properties.
proxy.base.url is a special property key that can be used to add the proxy base URL into the
header if the request was not sent through the proxy. It will automatically be injected into the
form-action and all fetch directives with a 'self' source when the
Inject proxy base URL into header feature is enabled. Only the protocol, host and port
of the proxy base URL will be added to the header. The X-Forwarded-Proto, X-Forwarded-Host,
X-Forwarded-Port, Forwarded and Host HTTP request headers are used to determine whether
or not the original request was sent to the proxy. Ensure that the proxy server is properly setting
these headers if the proxy base URL is being included in requests through the proxy and that is not
the desired behavior.
Note
Because the CSP is set so early in GeoServer’s request handling, a current limitation is that it cannot use proxy base URLs that are built from the HTTP request headers.
Leaving the directives blank will cause this rule to use the directives from the first preceding
rule with directives. No header value will be assigned if all preceding rules have no directives.
It does not matter whether a rule is enabled or disabled when searching preceding rules for
directives. The keyword NONE can be used to specify that no header value will be assigned to
requests that match this rule.
Testing¶
The Test Content Security Policy form allows a URL to be checked, reporting the CSP header value that would be set for a GET request to that URL. This form will test the current CSP configuration in the page to allow administrators to verify the changes before saving them to the configuration file.
Enter the URL to test in the Test URL text field and press the Test button to perform the test. The Content-Security-Policy header value text field will contain the CSP for the test URL with the string NONE being shown if no header would be set.
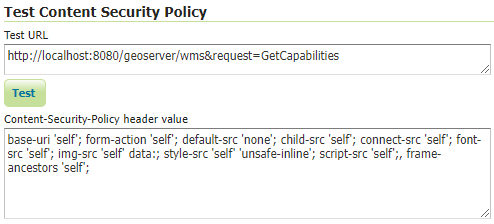
Test CSP with URL¶
System Administrator CSP Settings¶
CSP Configuration Overrides¶
The following settings override the Configuring CSP described above:
The
geoserver.csp.remoteResourcessystem property will override Allowed sources for remote web resources field if it has been set.The
geoserver.csp.frameAncestorssystem property will override Allowed frame-ancestors directive sources field if it has been set.
Fallback Directives¶
When an administrator is directly editing the CSP configuration file or uploading it through the
REST Resources API, it is possible to create a file that GeoServer cannot parse. In these cases,
GeoServer will fall back to using very strict header directives until the configuration file is
fixed. The geoserver.csp.fallbackDirectives property can be set either via Java system
property, command line argument (-D), environment variable or web.xml init parameter to change the
fallback directives from the default value:
base-uri 'none'; default-src 'none'; form-action 'none'; frame-ancestors 'none';
The keyword NONE can be used to specify that no header value will be assigned to requests when
there are CSP configuration errors.
CSP Strict¶
The environmental variable org.geoserver.web.csp.strict intended to allow access to Web Administration Console use during CSP Troubleshooting:
true: Content Security Policy violations will be blocked by the browser, with use of headerContent-Security-Policy.false: Content Security Policy violations will be reported in the developer tools console, with use headerContent-Security-Policy-Report-Only.This setting is intended to report CSP violations to the browser JavaScript console, so you can review and troubleshoot.
WFS GetFeatureInfo CSP Policy¶
The application property GEOSERVER_FEATUREINFO_HTML_SCRIPT controls the Content-Security-Policy for WFS GetFeatureInfo response limiting the use of fonts, images, style or script resources.
SELF: The default value; restricts template authors to content provided by GeoServer.UNSAFE: No restrictionWarning
Warning Allowing unsafe scripts could allow cross-site scripting attacks and should only be done if you can fully trust your template authors.
For more information see GetFeatureInfo Templates tutorial.
Serving Static Files¶
GeoServer allows serving static files from the GEOSERVER_DATA_DIR/www folder as an easy way to provide html, images or scripts alongside geospatial content.
The application property GEOSERVER_STATIC_WEB_FILES_SCRIPT controls the Content-Security-Policy for the static files location.
SELF: Restricts static file authors to content provided by GeoServer.UNSAFE: The default value, no restriction.
For more information see Serving Static Files.
References¶
See the following pages for details about CSP: